Software Stack
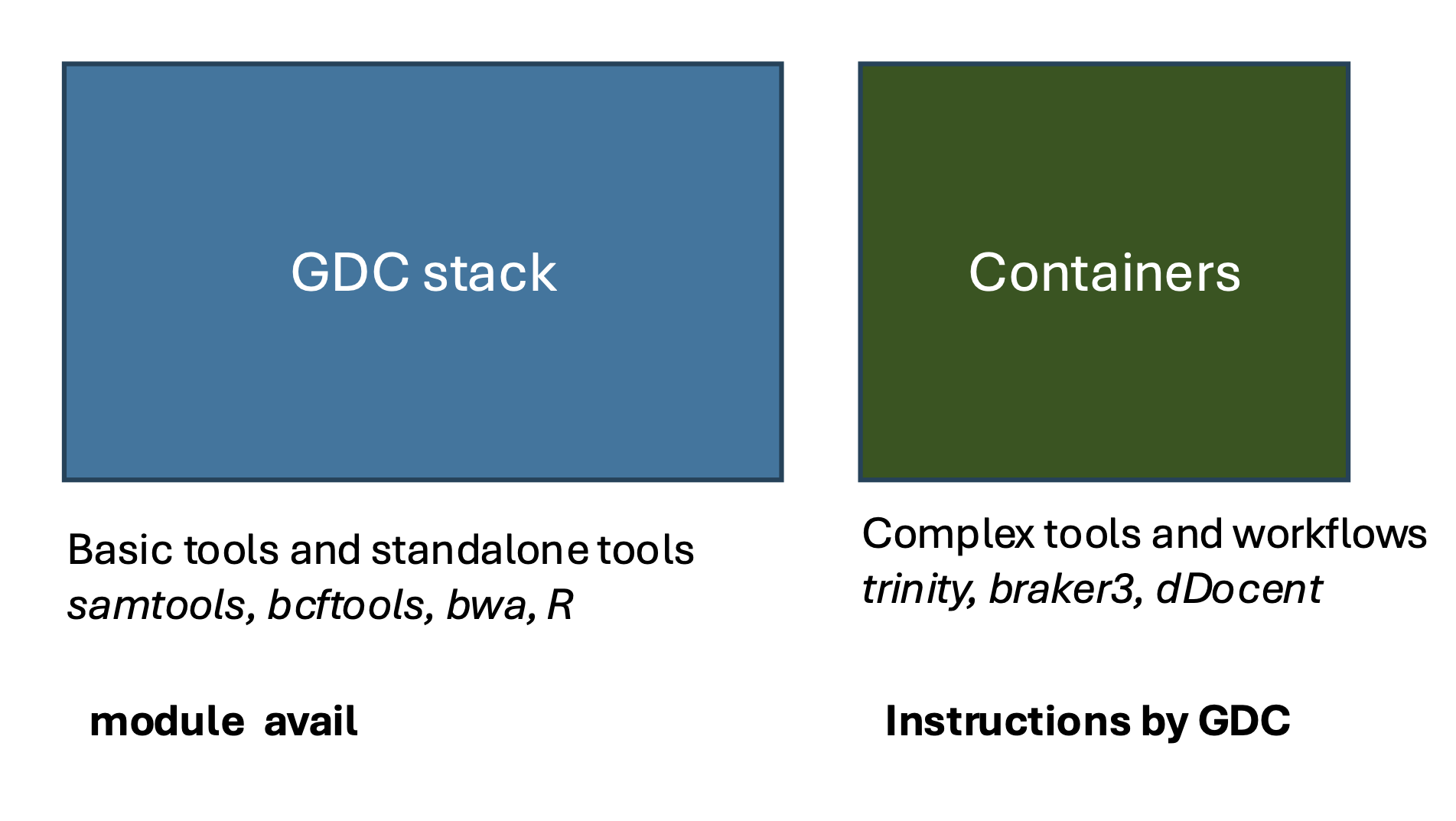
There are two main sources of tools on Euler. Standard tools can be loaded via lmod (module load). Make sure you source the GDC software stack (GDCstack.sh) to access the GDC specific tools. On the other hand, for more complex tools or pipelines, we offer container solutions. If you wish to use these, please contact the GDC for support.
Own Installation
For your own installation use your home ($HOME) and not GDC projects or GDC home.
Conda
It is not allowed to install conda environments on GDC home or GDC projects due to performance issues and the fact that they use a lot of inodes. More information can be found here. Either use your scratch or home (fast SSD drives). Conda environments can also be packed for archiving info or you can use tools such as Tykky to containerise it.
Software wrappers
Software wrappers are easy to use but a black box (e.g. snpArcher, ATLAS-Pipeline, DeepARG, Qime, R workflows like dada2). We do not recommend the use of such wrappers as they are usually extremely inefficient and sometimes impossible to optimise, which would be essential for use on Euler. If the jobs cannot be optimised (average CPU and memory usage > 50%), use the "sustaind" usage mode. We are happy to assist you in setting up your own workflow step by step.
Workflow managers
Workflow managers such as snakemake or Nextflow are tools for creating repeatable workflows. The problem is that the language is rather complex and it takes time to optimise all the sub-jobs. Both tools are available on Euler, but the GDC doesn't support them. If you want to use them yourself, you need to make sure that the jobs run efficiently. We recommend using simple bash scripts instead.
GDC stack
GDC software stack
| Application/version | Keyword |
|---|---|
| blast-plus/2.14.1 | Alignment |
| blast-plus/2.16.0 | Alignment |
| clustalw/2.1 | Alignment |
| diamond/2.1.7 | Alignment |
| hmmer/3.4-o2wkewh | Alignment |
| itsx/1.1.3 | Alignment |
| kraken2/2.1.2 | Alignment |
| mummer/4.0.0rc1 | Alignment |
| orfipy/0.0.4 | Annotation |
| prodigal/2.6.3 | Annotation |
| prokka/1.14.6 | Annotation |
| transdecoder/5.7.1 | Annotation |
| asstats/17.02 | Assembly |
| cap3/2015-02-11 | Assembly |
| cdhit/4.8.1 | Assembly |
| compleasm/0.2.7 | Assembly |
| flye/2.9.4 | Assembly |
| haphic/1.0.6 | Assembly |
| hifiasm/0.19.9 | Assembly |
| hifiasm/0.25.0 | Assembly |
| jellyfish/2.2.7 | Assembly |
| kmc/3.2.4 | Assembly |
| megahit/1.2.9 | Assembly |
| meryl/1.4.1 | Assembly |
| ragtag/2.1.0 | Assembly |
| rainbow/2.0.4 | Assembly |
| spades/4.0.0 | Assembly |
| yahs/1.2.2 | Assembly |
| openjdk/11.0.23_9 | Dependency |
| openjdk/17.0.11_9 | Dependency |
| openjdk/21.0.3_9 | Dependency |
| perl-bioperl/1.7.6 | Dependency |
| perl/5.38.0-qz5aop4 | Dependency |
| py-biopython/1.81 | Dependency |
| python/2.7.18 | Dependency |
| python/3.11.6 | Dependency |
| python/3.13.0 | Dependency |
| r/4.3.2 | Dependency |
| r/4.4.1 | Dependency |
| reportseff/2.7.6 | Dependency |
| bedops/2.4.41 | Manipulation |
| bedtools2/2.31.0 | Manipulation |
| csvtk/0.30 | Manipulation |
| dupsifter/1.3.0 | Manipulation |
| emboss/6.6.0 | Manipulation |
| gffread/0.12.7 | Manipulation |
| htslib/1.17-zmqlw7a | Manipulation |
| htslib/1.20 | Manipulation |
| htslib/1.22.1 | Manipulation |
| mapdamage/2.3.0 | Manipulation |
| mosdepth/0.3.8 | Manipulation |
| pear/0.9.6 | Manipulation |
| picard/2.26.3 | Manipulation |
| picard/3.1.1 | Manipulation |
| picard/3.3.0 | Manipulation |
| sambamba/1.0.1 | Manipulation |
| samblaster/0.1.24 | Manipulation |
| samtools/1.16.1 | Manipulation |
| samtools/1.17-yhme7vv | Manipulation |
| samtools/1.20 | Manipulation |
| samtools/1.22.1 | Manipulation |
| seqkit/0.10.1 | Manipulation |
| seqkit/2.8.2 | Manipulation |
| seqkit/2.10.0 | Manipulation |
| seqtk/1.4 | Manipulation |
| splitRef/0.1 | Manipulation |
| bbmap/39.01 | Mapping |
| bbmap/39.19 | Mapping |
| biscuit/1.6.1 | Mapping |
| bismark/0.24.1 | Mapping |
| bowtie2/2.5.1-s4wazon | Mapping |
| bowtie2/2.5.4 | Mapping |
| bwa-mem2/2.2.1 | Mapping |
| bwa-mem2/2.2.3 | Mapping |
| bwa/0.7.17 | Mapping |
| bwa/0.7.19 | Mapping |
| minimap2/2.26 | Mapping |
| minimap2/2.28 | Mapping |
| minimap2/2.30 | Mapping |
| urmap/1.0.1441 | Mapping |
| usearch/12-beta1 | Mapping |
| vsearch/2.22.1 | Mapping |
| aster/1.16 | Phylogenetics |
| beagle-lib/4.0.1 | Phylogenetics |
| fasttree/2.1.11 | Phylogenetics |
| iqtree/2.3.6 | Phylogenetics |
| iqtree/3.0.1 | Phylogenetics |
| mashtree/1.6.4 | Phylogenetics |
| newick_utils/12115 | Phylogenetics |
| rapidnj/2.3.3 | Phylogenetics |
| raxml-ng/1.2.2 | Phylogenetics |
| raxml/8.2.13 | Phylogenetics |
| vcf2phylip/2.3.0 | Phylogenetics |
| admixtools/7.0.2 | PopGen |
| admixture/1.3.0 | PopGen |
| angsd/0.935 | PopGen |
| angsd/0.940 | PopGen |
| atlas/0.9 | PopGen |
| baypass/2.41 | PopGen |
| beagle/5.4 | PopGen |
| distangsd/0.0.1 | PopGen |
| dsuite/0.5 | PopGen |
| easySFS/0.0.1 | PopGen |
| ezstructure/1.0.2 | PopGen |
| fsc/28 | PopGen |
| gcta/1.94.1 | PopGen |
| gemma/0.98.5 | PopGen |
| grendalf/0.6.2 | PopGen |
| jvarkit/65c451ad | PopGen |
| kmergwas/0.3 | PopGen |
| ngsadmix/0.1 | PopGen |
| ngsepcore/5.0.0 | PopGen |
| ngsld/1.2.0 | PopGen |
| ngsrelate/2.0 | PopGen |
| paleomix/1.3.7 | PopGen |
| pcangsd/1.2 | PopGen |
| pcangsd/1.36.2 | PopGen |
| pcaone/0.4.4 | PopGen |
| pixy/1.2.11 | PopGen |
| plink/1.07 | PopGen |
| plink/1.9 | PopGen |
| plink2/2.00a4.3 | PopGen |
| prune_graph/0.2.3 | PopGen |
| structure/2.3.4 | PopGen |
| treemix/1.13 | PopGen |
| winsfs/0.7.0 | PopGen |
| fastq-screen/0.15.3 | Quality Control |
| fastq-screen/0.16.0 | Quality Control |
| fastqc/0.12.1 | Quality Control |
| multiqc/1.30 | Quality Control |
| qualimap/2.2.1 | Quality Control |
| stacks/2.53 | RAD |
| stacks/2.68 | RAD |
| sra-tools/3.2.0 | Raw data |
| adapterremoval/2.3.3 | Read Filtering |
| cutadapt/4.9 | Read Filtering |
| fastp/0.20.1 | Read Filtering |
| fastp/0.23.4 | Read Filtering |
| fastp/0.24.0 | Read Filtering |
| fastp/1.0.1 | Read Filtering |
| fastx-toolkit/0.0.14 | Read Filtering |
| flash/1.2.11 | Read Filtering |
| printseq/1.2.4 | Read Filtering |
| trimgalore/0.6.10 | Read Filtering |
| trimmomatic/0.39 | Read Filtering |
| kallisto/0.48.0 | RNAseq |
| kallisto/0.51.1 | RNAseq |
| salmon/1.10.2 | RNAseq |
| sortmerna/4.3.7 | RNAseq |
| star/2.7.10b | RNAseq |
| star/2.7.11b | RNAseq |
| subread/2.0.6 | RNAseq |
| bcftools/1.16 | Variants |
| bcftools/1.20 | Variants |
| bcftools/1.22 | Variants |
| breseq/0.39.0 | Variants |
| freebayes/1.3.6 | Variants |
| freebayes/1.3.9 | Variants |
| gatk/3.8.1 | Variants |
| gatk/4.4.0.0 | Variants |
| gatk/4.6.1.0 | Variants |
| snpeff/2017-11-24 | Variants |
| snpeff/5.2.f | Variants |
| tiger/1.0 | Variants |
| vcfanno/0.3.5 | Variants |
| vcflib/1.0.13 | Variants |
| vcfpop/1.07b | Variants |
| vcftools/0.1.16-tc6l6nq | Variants |
| vcftools/0.1.17 | Variants |
To load the GDC software stack, you need to run the following command or add it to your submission script.
source /cluster/project/gdc/shared/stack/GDCstack.sh
Several versions of the main software stack are available on Euler. The GDC stack is based on stack/2024-05. There is no need to load any stack or gcc version if you have source the GDC stack.
Don't put the command directly into the bashrc file, but you can make an alias.
The following command will give you an overview of all the tools in the GDC stack.
module avail
Let's look again for samtools.
module avail samtools
As you can see there is now a newer version of samtools available.
samtools/1.16.1
samtools/1.20
samtools/1.22.1
Let's load samtools/1.22.1 the latest version.
module load samtools/1.22.1
Java tools
For some java tools like fastqc you need to load openjdk as well.
Euler stack
There is also a general Euler software stack containing older versions of some standard bioinformatic tools. It can be accessed as follows.
module load stack
GDC containers
For more complex tools or pipelines, we recommend to use container solutions that can be run via Apptainer.
Container rules
- Access to apptainer needs to be requsted.
- Containers should only be used when installation is impossible or very time consuming.
- Make sure that you use reliable container sources (e.g. Galaxy Depot Software Stack, BioContainers, Sylabs, Dockers).
- Containers cannot be modified/set-up on Euler but you can containerise a conda enviroment using tykky.
- If you setup/modify your own container, it is your responsibility to ensure that your container meets all security requirements.
- We do not provide support for tools inside a container. -> Contact the author(s)!
- Apptainer must be run on the Scratch (e.g. sif-file needs to be on the
$SCRATCH). - Sometimes jobs are not killed by slurm even if the job is no longer running. -> Monitor the job more regularly.
- The efficiency can be lower compared to a compiled tool, please be aware of this and adjust the requested resources accordingly.
- Writing your own scripts is generally more complex with Apptainer but an alias is useful.
Not all containers are constructed in the same way, but in many cases you can use the following recipe. If you have any problems, please contact the GDC for assistance.
Set up the environment
Add the follwing lines to your .bashrc file to set storage settings correctly.
export APPTAINER_CACHEDIR="$SCRATCH/.apptainer"
export APPTAINER_TMPDIR="${TMPDIR:-/tmp}"
Let's create an alias for our toolX.
alias "toolX=apptainer exec \
--bind ${SCRATCH} \
container.sif \
command_to_call_toolX"
Now you can call the container like any other tool.
toolX -h
Let's use a rather simple tool like Samtools for educational purposes.
cd ${SCRATCH}
#Let's download the container from galaxy to our Scratch.
wget https://depot.galaxyproject.org/singularity/samtools:0.1.19--3
mv samtools:0.1.19--3 samtools-1.9.sif
#Create alias
alias "sm=apptainer exec \
--bind ${SCRATCH} \
samtools-1.9.sif \
samtools"
#run samtools view
sm view -h
R
Available versions
module load r/4.3.2
module load r/4.4.1
Package installation
The commands for the installation of R packages depends on the repository. Use always the default path settings.
#### CRAN Repository
install.packages("package")
install.packages(c("packageA", "packageB"))
#### Bioconductor Repository
if (!requireNamespace("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE))
install.packages("BiocManager")
BiocManager::install("package")
#### GitHub
library(devtools)
devtools::install_github("link/to/package")
Python Tools
If you want to install your own Python tools, we strongly recommend that you use virtual environments that you have full control about different versions.
Installation
Let's install the tool cutadapt.
Go to your home
cd ${HOME}
Now we need to load the python module.
module load python/3.11.6
Now you can create a virtual environment called cutadapt.
python -m venv cutadapt
Now let's source the environment.
source ${HOME}/cutadapt/bin/activate
Now you can install the tool via pip.
pip install cutadapt
Use
In your submission script, you would add the following lines
module load python/3.11.6
source ${HOME}/cutadapt/bin/activate
cutadapt -h
Databases
Databases are difficult to maintain when many users are involved. Maintaining them is more expensive than simply downloading them again, especially if they are pre-built. Each user should download the databases directly to the Scratch, run the analysis and then delete them again.
Only the large NCBI Blast databases are stored centrally and maintained by the Cluster Support.
/cluster/project/clcgenomics/CLC_BLAST_DB
With the follwing command you can blast against the nt database.
blastn -task blastn -query query.fata \
-db /cluster/project/clcgenomics/CLC_BLAST_DB/nt -out query_nt.tab \
-outfmt '6 qseqid sseqid pident length mismatch gapopen qstart qend sstart send evalue bitscore stitle sscinames sskingdoms'